Binary Tree Traversals
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1406 Accepted Submission(s): 655
Problem Description
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the
vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
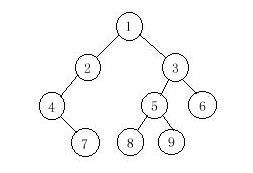
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating
the preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
Output
For each test case print a single line specifying the corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
9
1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6
4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
Source
Recommend
lcy
本质就是知道二叉树的前序和中序求后序
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int preorder[1005];
int inorder[1005];
void dfs(int pre,int in,int size,bool flag)
{
int i;
if(size==1) //如果有左子树或右子树,就直接输出
{
printf("%d ",preorder[pre]);
return ;
}
if(size<=0) //没有左子树或右子树,则返回上层,遍历右子树或者根
return ;
for(i=0;preorder[pre]!=inorder[in+i];i++);//查找根节点在中序中的位置
dfs(pre+1,in,i,false); //左子树的遍历
dfs(pre+i+1,in+i+1,size-i-1,false); //右子树的遍历
if(flag) //输出根节点
printf("%d\n",preorder[pre]); //整个树的根节点
else
printf("%d ",preorder[pre]); //一般的根节点
}
int main()
{
int n,i;
while(cin>>n)
{
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&preorder[i]);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&inorder[i]);
dfs(1,1,n,true);
}
return 0;
}
分享到:









相关推荐
HDOJ题目分类HDOJ题目分类HDOJ题目分类
ACM ICPC HDOJ1002
hdoj1001标程
ACM ICPC HDOJ1001
hdoj上的资源,代码有注释,很不错的哦
hdoj1004,解题代码,答案代码,欢迎下载
ACM ICPC HDOJ1003
ACM ICPC HDOJ1008
杭州电子科技大学hdoj1002,大整数相加问题
杭州电子科大HDOJ
c语言 最短路 是hdoj上的一个最短路问题,写的很牛
ACM ICPC HDOJ1000
hdoj解题代码,题目为1000-1050
一些HDOJ上的DP题目的小总结,但愿能帮到那些想专攻DP的人吧
codj,hdoj的源码(50-60题)
hdoj 2013 多校训练3标程+解题报告
HDOJ 源代码 包含几百道HDOJ题目源码
hdoj1005 Number Sequence, 杭州电子科技大学oj题目代码
杭电OJ(1000-1099) AC 代码
HDOJ使用指南——公开版.docHDOJ使用指南——公开版.docHDOJ使用指南——公开版.doc